Jewish immigration to israel crossword – Jewish immigration to Israel, a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, has shaped the history, culture, and identity of both the Jewish people and the State of Israel. This comprehensive exploration delves into the motivations, waves, impact, and international perspectives surrounding this pivotal migration.
From the historical events that ignited the desire for a Jewish homeland to the challenges and triumphs faced by immigrants, this article unravels the intricate tapestry of Jewish immigration to Israel, shedding light on its profound significance for the Jewish state and the global Jewish community.
Jewish Immigration to Israel: Jewish Immigration To Israel Crossword
Jewish immigration to Israel has been a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has shaped the history and demographics of the Jewish people and the State of Israel. This article provides an overview of the historical context, motivations, waves, impact, challenges, cultural exchange, international perspectives, and legacy of Jewish immigration to Israel.
Historical Context, Jewish immigration to israel crossword
The history of Jewish immigration to Israel can be traced back to the late 19th century, when the Zionist movement emerged as a response to rising anti-Semitism and persecution of Jews in Europe. The movement advocated for the establishment of a Jewish state in the Land of Israel, which was then under Ottoman rule.
In 1917, the British government issued the Balfour Declaration, which expressed support for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. After World War I, the British Mandate for Palestine was established, which facilitated the immigration of Jewish settlers to the region.
Motivations for Immigration
The motivations for Jewish immigration to Israel were varied and complex, but they can be broadly categorized into religious, political, economic, and social factors.
- Religious motivations:Many Jews immigrated to Israel out of a deep religious connection to the Land of Israel, which is considered the Promised Land in Jewish tradition.
- Political motivations:Jews who experienced persecution and discrimination in Europe sought refuge in Israel, where they could live in a Jewish state with self-determination.
- Economic motivations:Economic opportunities in Israel attracted many Jewish immigrants, especially during the early years of the state’s development.
- Social motivations:Jews who faced social isolation and discrimination in their home countries sought a sense of community and belonging in Israel.
Waves of Immigration
Jewish immigration to Israel occurred in several waves, each with its own unique characteristics and demographics.
- First Aliyah (1881-1903):This wave consisted of approximately 30,000 Jewish immigrants, mostly from Eastern Europe, who were motivated by religious and economic factors.
- Second Aliyah (1904-1914):This wave saw the immigration of approximately 40,000 Jews, many of whom were socialists and labor Zionists who sought to build a Jewish homeland through agricultural settlement.
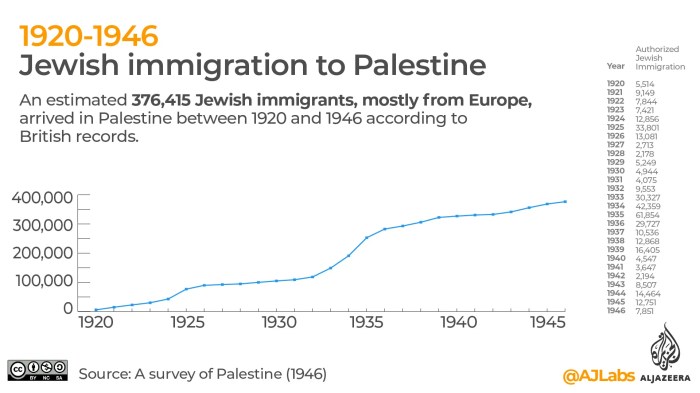
- Third Aliyah (1919-1923):This wave consisted of approximately 40,000 Jewish immigrants, mostly from Eastern Europe, who arrived after World War I and the Balfour Declaration.
- Fourth Aliyah (1924-1929):This wave saw the immigration of approximately 80,000 Jews, mostly from Poland, who were motivated by economic and political factors.
- Fifth Aliyah (1930-1939):This wave consisted of approximately 250,000 Jewish immigrants, mostly from Germany, who fled the Nazi regime.
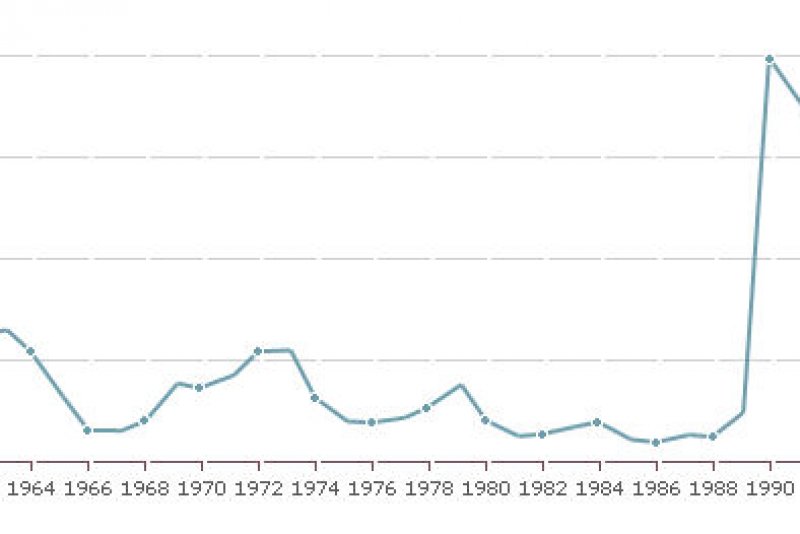
- Sixth Aliyah (1948-1951):This wave saw the immigration of approximately 600,000 Jews, many of whom were Holocaust survivors and refugees from Arab countries.
- Seventh Aliyah (1951-1960):This wave consisted of approximately 350,000 Jewish immigrants, mostly from North Africa and the Middle East.
- Eighth Aliyah (1961-1973):This wave saw the immigration of approximately 250,000 Jews, mostly from the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe.
- Ninth Aliyah (1973-1989):This wave consisted of approximately 150,000 Jewish immigrants, mostly from the Soviet Union and Ethiopia.
- Tenth Aliyah (1990-2000):This wave saw the immigration of approximately 1 million Jews, mostly from the former Soviet Union.
- Eleventh Aliyah (2000-present):This wave has seen the immigration of approximately 250,000 Jews, mostly from France, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Impact on Israeli Society
Jewish immigration has had a profound impact on Israeli society, shaping its demographics, economy, and culture.
- Demographic impact:Jewish immigration has significantly increased the population of Israel, with Jews now constituting approximately 75% of the total population.
- Economic impact:Jewish immigrants have contributed to the development of Israel’s economy, bringing with them skills, knowledge, and capital.
- Cultural impact:Jewish immigration has led to a vibrant and diverse Israeli culture, which incorporates elements from different Jewish communities around the world.
FAQ Resource
What were the primary motivations for Jewish immigration to Israel?
Religious, political, economic, and social factors, including persecution, anti-Semitism, and the desire for self-determination, drove Jewish immigration to Israel.
How many waves of Jewish immigration to Israel have there been?
There have been several waves of Jewish immigration to Israel, including the First Aliyah (1882-1903), the Second Aliyah (1904-1914), the Third Aliyah (1919-1923), and the Fourth Aliyah (1924-1929).
What were some of the challenges faced by Jewish immigrants in Israel?
Jewish immigrants faced challenges such as language barriers, cultural differences, economic integration, and discrimination.