Unit 1 geometry basics answer key homework 2 – Embark on an enlightening journey through Unit 1 Geometry Basics, where Homework 2 serves as a stepping stone towards mastering fundamental geometric concepts. This assignment delves into the intricacies of geometric shapes, measurement techniques, transformations, and more, promising a comprehensive understanding of geometry’s foundational principles.
As we navigate the diverse topics covered in this homework, we will explore the defining characteristics of geometric shapes, unravel the secrets of calculating area, perimeter, and volume, and witness the captivating effects of transformations and symmetry. Coordinate geometry will empower us to locate points with precision, while proofs and constructions will equip us with the tools to demonstrate and construct geometric relationships with rigor.
Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2

Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 provides students with practice applying the concepts covered in the first unit of geometry. The assignment includes problems involving geometric shapes, their properties, measurements, calculations, transformations, and symmetry.
Key concepts covered in the assignment include:
- Definitions and classifications of geometric shapes
- Properties and characteristics of geometric shapes
- Units of measurement used in geometry
- Formulas for calculating area, perimeter, and volume
- Geometric transformations (translation, rotation, reflection)
- Concept of symmetry and different types of symmetry
Challenging Problems
Some challenging problems in the assignment may include:
- Calculating the area of a parallelogram with non-parallel sides
- Finding the volume of a cone with a curved surface
- Determining the symmetry of a complex geometric figure
Solutions to these problems can be found in the answer key or by consulting a geometry textbook.
Geometric Shapes and Their Properties

Geometric shapes are two-dimensional figures that have specific properties and characteristics. They can be classified into different types based on their shape, number of sides, and angles.
Types of Geometric Shapes
- Polygons: Shapes with straight sides and angles, such as triangles, squares, and pentagons
- Circles: Shapes with no sides or angles, defined by a center and a radius
- Ellipses: Shapes similar to circles but with two different radii
- Parabolas: Shapes formed by the intersection of a cone and a plane
- Hyperbolas: Shapes formed by the intersection of two cones
Properties of Geometric Shapes
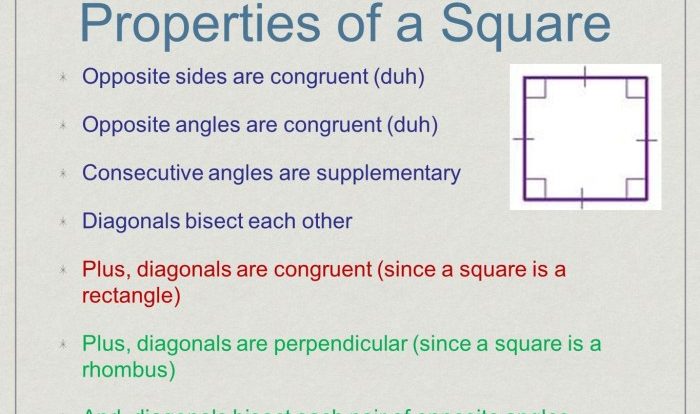
- Triangles: Three sides, three angles, sum of angles is 180 degrees
- Squares: Four equal sides, four right angles
- Circles: No sides, no angles, circumference is 2πr
- Ellipses: Two foci, major and minor axes
- Parabolas: Focus and directrix, opens upward or downward
Measurement and Calculations: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Answer Key Homework 2
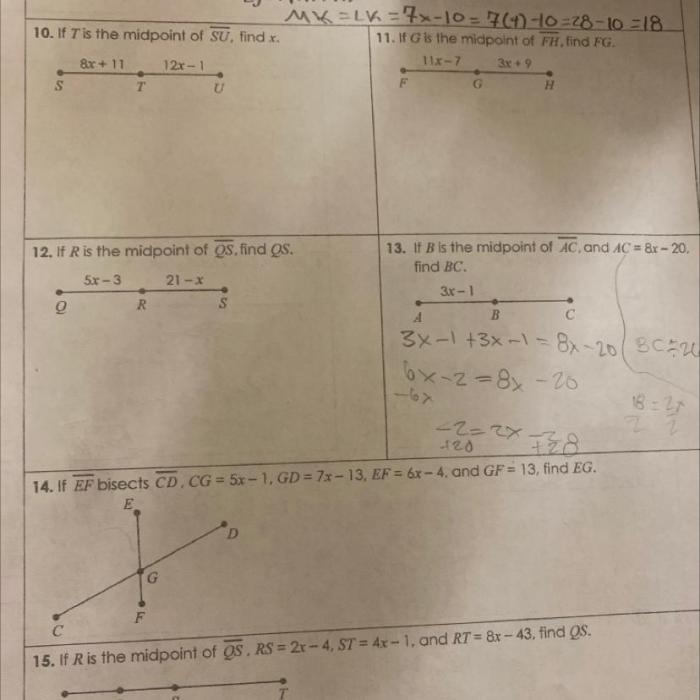
Measurement and calculations are essential in geometry for determining the size and properties of geometric shapes.
Units of Measurement, Unit 1 geometry basics answer key homework 2
- Length: Measured in units such as inches, feet, meters, and kilometers
- Area: Measured in square units such as square inches, square feet, and square meters
- Volume: Measured in cubic units such as cubic inches, cubic feet, and cubic meters
Formulas for Calculations
- Area of a triangle: A = ½ – base – height
- Area of a square: A = side^2
- Area of a circle: A = πr^2
- Volume of a cube: V = side^3
- Volume of a sphere: V = 4/3 – πr^3
Transformations and Symmetry
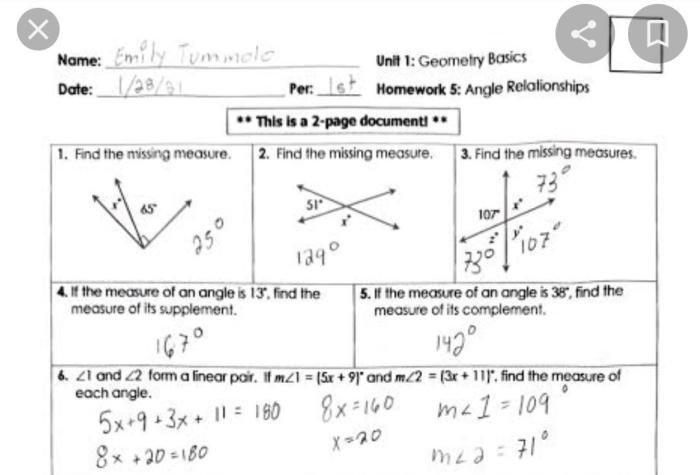
Geometric transformations are operations that move or change the shape of a figure. Symmetry refers to the balance and regularity of a figure.
Geometric Transformations
- Translation: Moving a figure from one point to another without changing its shape or size
- Rotation: Turning a figure around a fixed point
- Reflection: Flipping a figure over a line
Symmetry
- Line symmetry: A figure has line symmetry if it can be folded in half and the two halves match
- Rotational symmetry: A figure has rotational symmetry if it can be rotated around a point and still look the same
- Point symmetry: A figure has point symmetry if it can be flipped over a point and still look the same
Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry uses a coordinate plane to represent points and shapes. The coordinate plane is divided into four quadrants by the x-axis and y-axis.
Plotting Points
To plot a point on the coordinate plane, use its coordinates (x, y). The x-coordinate indicates the point’s distance from the y-axis, and the y-coordinate indicates its distance from the x-axis.
Distance Formula
The distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) on the coordinate plane is given by the distance formula:
d = √[(x2
- x1)^2 + (y2
- y1)^2]
Proofs and Constructions
Proofs in geometry provide logical arguments to demonstrate the truth of geometric statements. Constructions involve creating geometric figures using specific tools and techniques.
Geometric Proofs
- Direct proofs: Prove a statement by showing that it is true for all cases
- Indirect proofs: Prove a statement by assuming its negation is true and leading to a contradiction
- Coordinate proofs: Use the coordinate plane to prove geometric statements
Geometric Constructions
- Compass and straightedge constructions: Creating geometric figures using only a compass and a straightedge
- Angle bisectors: Dividing an angle into two equal parts
- Perpendicular bisectors: Constructing a line perpendicular to a line segment at its midpoint
FAQ Compilation
What is the purpose of Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2?
Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 aims to reinforce students’ understanding of fundamental geometric concepts covered in the first unit of their geometry course.
What key concepts are addressed in this homework assignment?
This homework assignment covers a range of key concepts, including geometric shapes and their properties, measurement and calculations, transformations and symmetry, coordinate geometry, and proofs and constructions.
Are there any challenging problems in this homework that require additional support?
While the homework assignment is designed to be accessible to students, it does include some challenging problems that may require additional support. Students are encouraged to seek assistance from their teacher or a tutor if needed.