Embarking on an exploration of chemical reactions, the decomposition and synthesis reactions worksheet serves as an invaluable resource for students seeking to delve into the fascinating world of chemistry. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate details of decomposition and synthesis reactions, providing a solid foundation for further exploration and understanding.
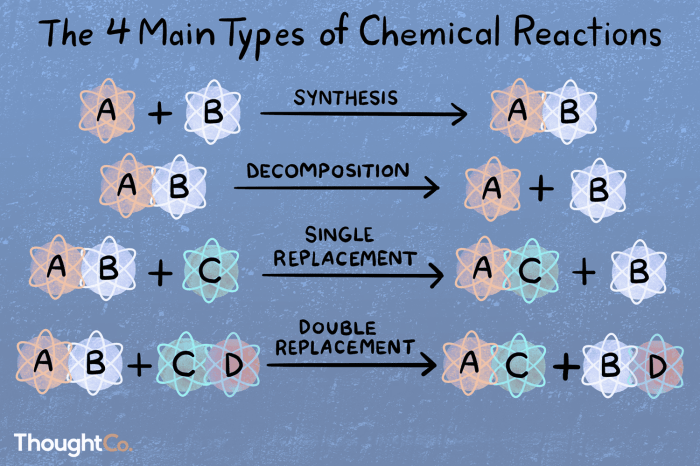
Decomposition reactions, characterized by the breakdown of a single compound into simpler substances, and synthesis reactions, involving the formation of a new compound from simpler substances, are fundamental concepts in chemistry. This worksheet delves into the intricacies of these reactions, exploring the factors that influence their rates and providing real-world examples to illustrate their significance.
Decomposition Reactions

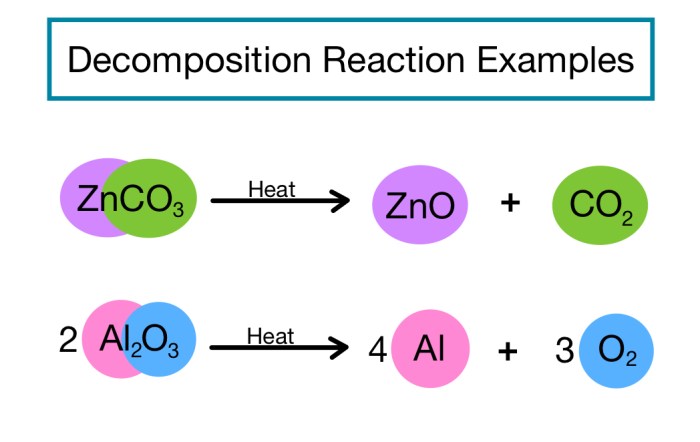
Decomposition reactions are chemical reactions in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. These reactions are typically endothermic, meaning they require energy to occur.
Decomposition reactions can be classified into three types: thermal decomposition, photolysis, and electrolysis. Thermal decomposition occurs when a compound is heated to a high temperature, causing it to break down. Photolysis occurs when a compound is exposed to light, causing it to break down.
Electrolysis occurs when an electric current is passed through a compound, causing it to break down.
The rate of a decomposition reaction is affected by several factors, including the temperature, the concentration of the reactant, and the presence of a catalyst.
Examples of Decomposition Reactions
- The decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen: 2H 2O → 2H 2+ O 2
- The decomposition of calcium carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide: CaCO 3→ CaO + CO 2
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen: 2H 2O 2→ 2H 2O + O 2
Synthesis Reactions
Synthesis reactions are chemical reactions in which two or more simpler substances combine to form a single more complex substance. These reactions are typically exothermic, meaning they release energy as they occur.
Synthesis reactions can be classified into two types: combination reactions and decomposition reactions. Combination reactions occur when two or more elements combine to form a compound. Decomposition reactions occur when a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
The rate of a synthesis reaction is affected by several factors, including the temperature, the concentration of the reactants, and the presence of a catalyst.
Examples of Synthesis Reactions, Decomposition and synthesis reactions worksheet
- The synthesis of water from hydrogen and oxygen: 2H 2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
- The synthesis of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine: 2Na + Cl 2→ 2NaCl
- The synthesis of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen: N 2+ 3H 2→ 2NH 3
Worksheet Design
A worksheet on decomposition and synthesis reactions should include a variety of problems that require students to apply their knowledge of these reactions. The worksheet should also include clear instructions and a table to organize the reactions and their products.
Here is an example of a worksheet problem:
Write the balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Here is an example of a table that could be used to organize the reactions and their products:
| Reaction | Products |
|---|---|
| 2H2O → 2H2 + O2 | Hydrogen and oxygen |
| CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 | Calcium oxide and carbon dioxide |
| 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 | Water and oxygen |
Assessment
An assessment on decomposition and synthesis reactions should include a variety of question types, such as multiple choice, short answer, and essay. The assessment should also include a rubric for grading student responses.
Here is an example of a multiple choice question:
Which of the following is an example of a decomposition reaction?
- 2H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
- CaCO 3→ CaO + CO 2
- 2H 2O 2→ 2H 2O + O 2
Here is an example of a short answer question:
Explain the difference between a decomposition reaction and a synthesis reaction.
Here is an example of an essay question:
Discuss the factors that affect the rate of a decomposition reaction.
Extensions: Decomposition And Synthesis Reactions Worksheet
Additional activities or resources that can be used to extend student learning on decomposition and synthesis reactions include:
- Hands-on experiments, such as the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide or the synthesis of water
- Simulations, such as the PhET Decomposition Reactions simulation
- Online resources, such as the Khan Academy Decomposition and Synthesis Reactions video
The potential applications of decomposition and synthesis reactions in real-world settings include:
- The production of fuels, such as hydrogen and methane
- The production of fertilizers, such as ammonia and urea
- The production of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene
FAQ
What is the difference between decomposition and synthesis reactions?
Decomposition reactions involve the breakdown of a single compound into simpler substances, while synthesis reactions involve the formation of a new compound from simpler substances.
What factors affect the rate of decomposition reactions?
Factors that affect the rate of decomposition reactions include temperature, concentration, surface area, and the presence of a catalyst.
How can I use the decomposition and synthesis reactions worksheet?
The worksheet provides a variety of activities, explanations, and questions to help students understand decomposition and synthesis reactions. It can be used as a supplement to classroom instruction or as a self-study resource.
